Introduction
Thrombosis, abscesses, and embolic infections are interconnected medical conditions that can lead to severe health complications if not managed properly. Understanding these conditions is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. This guide explores each of these issues in detail, providing you with the knowledge needed to identify symptoms, understand causes, and seek appropriate care.
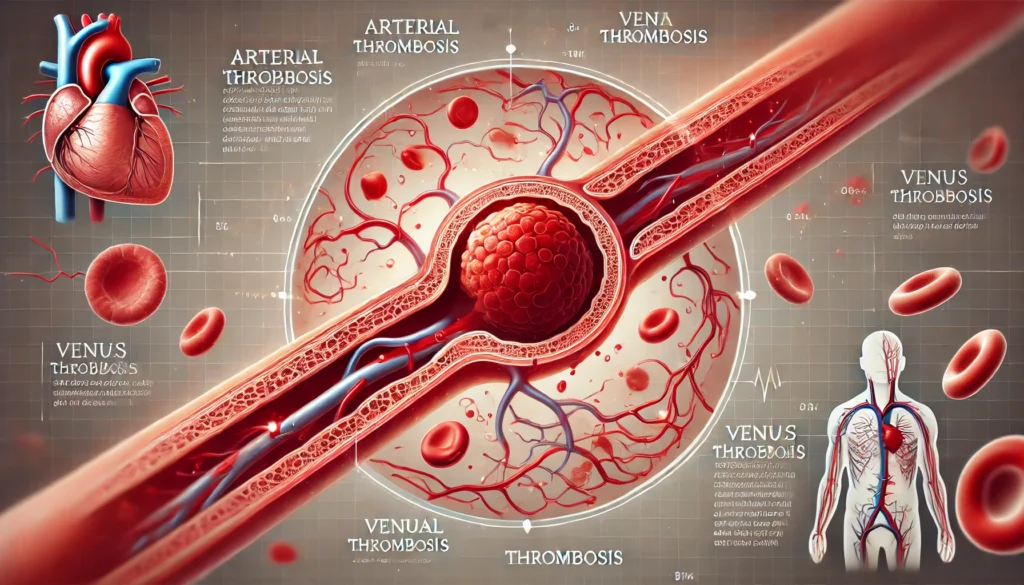
What Is Thrombosis?
Definition
Thrombosis refers to the formation of a blood clot within a blood vessel. This clot, known as a thrombus, can partially or completely block blood flow, leading to complications such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE).
Types of Thrombosis
- Arterial Thrombosis: Occurs in arteries, leading to heart attacks or strokes.
- Venous Thrombosis: Develops in veins, often in the legs, causing conditions like DVT.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Genetic predisposition: Conditions like Factor V Leiden increase clotting risk.
- Lifestyle factors: Prolonged immobility, smoking, and obesity.
- Medical conditions: Cancer, heart disease, and pregnancy.
Symptoms
- Swelling and pain in the affected area.
- Red or discolored skin.
- Warmth around the clot site.
Diagnosis
Doctors may use Doppler ultrasound, blood tests (D-dimer), or imaging techniques like CT scans to confirm thrombosis.
Treatment
- Medications: Anticoagulants like warfarin or heparin.
- Surgical intervention: In severe cases, thrombectomy or catheter-directed thrombolysis.
- Lifestyle changes: Exercise, hydration, and dietary adjustments.
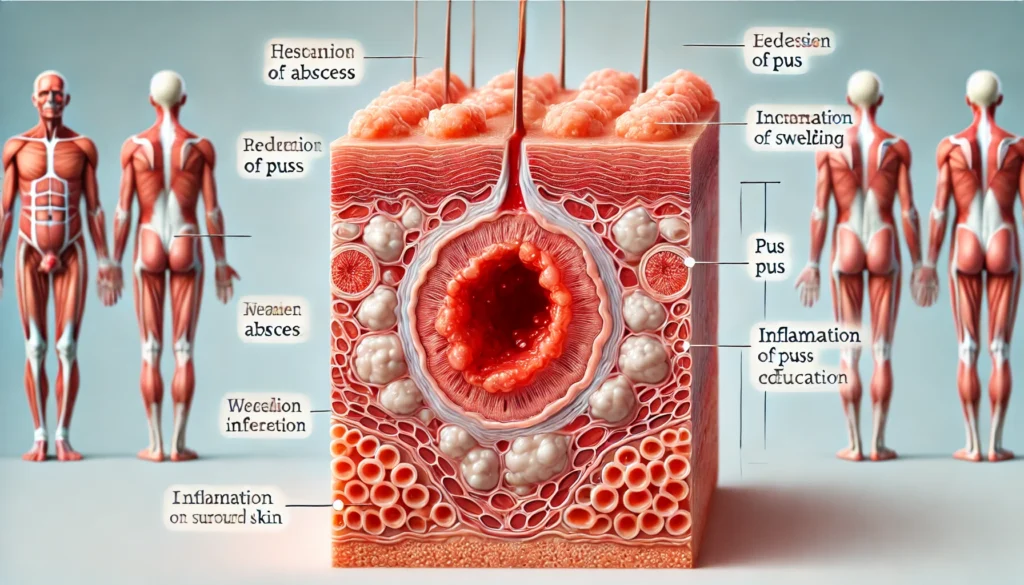
What Is an Abscess?
Definition
An abscess is a localized collection of pus caused by a bacterial infection. It can form in various parts of the body, such as the skin, gums, or internal organs.
Common Causes
- Bacterial infections: Staphylococcus aureus is a common culprit.
- Foreign objects: Splinters or medical devices.
- Weakened immune system: Due to conditions like diabetes or HIV.
Symptoms
- Redness, swelling, and pain at the site.
- Presence of pus or fluid drainage.
- Fever and chills if the infection spreads.
Diagnosis
Doctors often use physical examinations, imaging tests like ultrasound, or fluid culture analysis to diagnose abscesses.
Treatment
- Drainage: Surgical removal of pus.
- Antibiotics: To control bacterial infection.
- Home care: Warm compresses and hygiene maintenance.
Understanding Embolic Infections
Definition
An embolic infection occurs when infected particles, such as a septic embolus, travel through the bloodstream and block blood flow in distant organs.
Common Sources
- Infective endocarditis: Infection of the heart lining.
- Deep vein thrombosis: A clot that becomes infected.
- Abscesses: Bacteria spreading from localized infections.
Symptoms
- Fever and chills.
- Shortness of breath or chest pain (if affecting the lungs).
- Neurological symptoms like confusion or stroke (if affecting the brain).
Diagnosis
- Blood cultures: To identify the causative organism.
- Imaging tests: MRI, CT scan, or echocardiography.
Treatment
- Antimicrobial therapy: Tailored to the specific organism.
- Surgical intervention: Removal of infected tissue or drainage of abscesses.
Interrelationship Between Thrombosis, Abscesses, and Embolic Infections
These conditions are often interconnected. For instance, an untreated abscess can lead to bacteremia, which may cause septic thrombophlebitis (infected blood clots). Similarly, septic emboli can travel to vital organs, causing life-threatening complications like lung abscesses or brain abscesses. Early intervention is critical to prevent such cascading effects.
Prevention Strategies
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Stay active to prevent blood clots.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid smoking.
- Medical Interventions:
- Regular screenings for at-risk individuals.
- Prophylactic medications for clot prevention.
- Hygiene Practices:
- Proper wound care to prevent abscess formation.
- Prompt treatment of infections to avoid systemic spread.
Complications and Prognosis
Unmanaged thrombosis, abscesses, or embolic infections can result in:
- Chronic pain and swelling.
- Organ damage or failure.
- Long-term disability or death.
However, with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many individuals recover fully. Long-term follow-up and lifestyle adjustments play a key role in minimizing recurrence.
Patient Stories
Real-life accounts provide invaluable insights. For example:
- A patient with deep vein thrombosis prevented severe complications by recognizing early symptoms.
- Another individual’s lung abscess resolved successfully with a combination of antibiotics and surgical drainage.
FAQs
- Can thrombosis occur without noticeable symptoms?
Yes, some cases, especially in deep veins, may be asymptomatic. - How can I differentiate between a cyst and an abscess?
An abscess is usually painful, warm, and associated with infection, while a cyst is a non-infected fluid-filled sac. - Are embolic infections contagious?
No, but the underlying infection may spread if not treated. - What foods help reduce the risk of thrombosis?
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, garlic, and leafy greens promote blood circulation and reduce clot risk. - How long does it take to recover from a thrombosis-related complication? Recovery time varies, ranging from weeks to months, depending on the severity and treatment.
Conclusion
Thrombosis, abscesses, and embolic infections are serious conditions that require prompt attention. Understanding their symptoms, causes, and treatments is essential for effective management. By adopting preventive measures and seeking early medical intervention, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications. Stay proactive about your health to lead a fulfilling life.
Recommended Articles
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding and Managing a Patchy Beard
Smartbook HJC160 Review: Everything You Need to Know about the HJC173 Model and Its Camera
Sliuce 1088 by Gold: The Ultimate Guide to Gold Prospecting Efficiency
A Comprehensive Guide to Furniture Transfers Rub On
The Ultimate Guide to Nattienut9